Faced with financial, logistical, and geopolitical challenges, Riyadh has been forced to review its ambitious project, The Line, and critically reassess “economic normalization” with Israel.

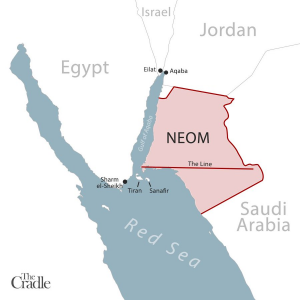
Launched in 2017, Saudi Arabia’s NEOM, a sprawling high-tech development on the northwestern Red Sea coast, was introduced as the crown jewel of Vision 2030.
This futuristic desert megaproject, extending over some Jordanian and Egyptian territory, was cast as a bold leap toward economic diversification under the leadership of Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman (MbS). But, recent geopolitical setbacks have raised significant concerns about the viability of some of NEOM’s components.
Initially celebrated for its revolutionary design, The Line, a linear city within NEOM, was to redefine urban living. Yet, recent reports suggest a dramatic scaling back. Earlier this month, Bloomberg revealed a massive reduction in the metropolis’ scope – from 105 to 1.5 miles – and a decrease in likely inhabitants from 1.5 million to fewer than 300,000 by 2030. Furthermore, funding uncertainties and workforce reductions indicate a project in jeopardy.
While this adjustment does not signify a wholesale failure of Vision 2030, it does prompt a re-evaluation of the project’s most ambitious elements.
Experts suggest that The Line’s original scale was overly optimistic, lacking the necessary urban infrastructure for such an innovative endeavor. Financial and geopolitical challenges, including regional instability and insufficient foreign direct investment, further complicate NEOM’s future.
Not so straight-forward
The drastic downsizing of The Line “appears to be a reassessment of timeline feasibility,” Dr Robert Mogielnicki, a senior resident scholar at the Arab Gulf States Institute in Washington, tells The Cradle. “There are many experimental, world-first dimensions within the NEOM gigaproject, and some are eventually going to need rightsizing or rethinking.”
Also speaking to The Cradle, Dr Kristian Coates Ulrichsen, a Baker Institute Fellow at Rice University, believes the project’s contraction to be a good thing:
Reports that The Line may be scaled back significantly is actually a positive move if it injects greater realism into a project whose initial scale appeared fanciful and difficult to translate into reality. Greater pragmatism in designing and delivering the gigaprojects associated with Vision 2030 is a good thing and means there is a greater likelihood of the projects making it off the drawing board.
Given financial and economic factors, The Line was never feasible as initially presented. Ultimately, the amount of wealth the Saudis generate from oil is not enough to finance the most ambitious of MbS’ Vision 2030 projects. And Riyadh has not been able to lure the levels of foreign direct investment needed to make these extremely expensive vanity projects realizable.
“The vast scope of [The Line] always struck me and many other observers as aspirational rather than realistic,” explains Gordon Gray, the former US ambassador to Tunisia.
Speaking to The Cradle, Ryan Bohl, a Middle East and North African analyst at risk intelligence company RANE, says:
I’d argue that the goals for The Line were unrealistic from the start, given that there’s virtually no urban infrastructure in the area, and it’s very difficult for cities to be started from scratch like that, regardless of the amount of investment poured in. Even if Saudi Arabia had, for example, done something extreme like declare NEOM to be their new capital city, it would still probably struggle to attract residents as we’ve seen from other historical examples like Brazil’s shift of its capital to Brasília.
Nonetheless, The Line and other singular projects had a purpose that was not necessarily about actually implementing the projects themselves. “The point of The Line, in particular, was to create a raison de parler – for people to actually talk about Saudi Arabia, to create a massive public debate globally where people are saying there’s something amazing happening in the desert,” Dr Andreas Krieg, an associate professor at King’s College London, tells The Cradle.
It attracts attention. That sort of discourse – positive or negative – creates a buzz. That buzz was supposed to attract investors who wanted to be a part of this, help Saudi Arabia build a city of the future, and try to do something completely outlandish and absolutely unconventional.
Gaza: a wrench in the works
The leadership in Riyadh has understood that the success of Vision 2030 heavily depends on attracting substantial foreign direct investment into the Kingdom. Ultimately, stability in Saudi Arabia and the wider West Asian region is crucial.
Consequently, Riyadh’s recent foreign policy has been less ideological, focusing instead on maintaining amicable terms with all major players in West Asia to advance Saudi business, commercial, and economic interests.
Within this context, Riyadh has worked to reach a peace deal with Yemen’s Ansarallah resistance movement, made an effort to preserve the Beijing-brokered 2023 Saudi–Iranian détente, restored relations with Qatar and Syria, and mended fences with Turkiye.
Therefore, beyond financial and economic constraints that require a reassessment of the most ambitious Vision 2030 projects, such as The Line, Israel’s brutal six-month war on Gaza and the expansion of that conflict into the Red Sea have created headwinds for Saudi Arabia’s geoeconomic plans.
As Arhama Siddiqa, a Research Fellow at the Institute of Strategic Studies Islamabad, explains to The Cradle:
Given the current instability in the Red Sea region, investors may hesitate to support a large-scale project like NEOM due to perceived risks. Even if the direct security threat to NEOM is minimal, the overall instability in the area can deter investors from committing substantial resources to a long-term venture. Additionally, the broader [West Asia] conflict further complicates the situation, adding another layer of uncertainty. Addressing these security concerns could require Saudi Arabia to allocate more resources to regional security measures, potentially diverting funds from the NEOM project.
There is no denying that Saudi Arabia’s economic diversification agenda is vulnerable to naval operations in the Red Sea. NEOM and other Red Sea projects require vessels to be able to freely travel from the Gulf of Aden through the Bab al-Mandab and up to Saudi Arabia’s west coast.
The Gaza war’s potential spillover into this vital waterway continues to raise concerns for Saudi officials about the impact on the Kingdom’s Vision 2030.
These dynamics help explain Riyadh’s frustration with the White House for not leveraging its influence over Israel to negotiate a ceasefire in Gaza. It has led to Saudi Arabia’s decision to abstain from joining any US-led security initiatives and military operations in the Red Sea and Yemen.
The Israel–NEOM connection
Israel’s geographic proximity to northwestern Saudi Arabia, its technological advancement, and its vibrant startup culture position the occupation state as a promising partner for Vision 2030 and the NEOM project, particularly in biotechnology, cybersecurity, and manufacturing.
Writing in March 2021, Dr Ali Dogan, previously a Research Fellow at the Leibniz-Zentrum Moderner Orient, went as far as arguing that “relations with Israel are necessary for Saudi Arabia to complete NEOM.”
Dr Mohammad Yaghi, a research fellow at Germany’s Konrad Adenauer Stiftung, similarly stated that NEOM “requires peace and coordination with Israel, especially if the city is to have a chance of becoming a tourist attraction.”
However, Saudi Arabia’s leadership role in the Islamic world, exemplified by the monarch’s title as the “Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques,” makes any formal normalization of relations with Tel Aviv highly sensitive.
Initially, it was thought that while the UAE and Bahrain could establish overt relations with Israel, Saudi Arabia would continue to engage covertly, ensuring essential collaborations like those rumored in the tech sector could progress discreetly.
An example being in June 2020, when controversy arose over Saudi Arabia’s alleged engagement with an Israeli cybersecurity firm, which the Saudi embassy later denied.
Yet, almost seven months into Israel’s campaign to annihilate Gaza, can Saudi Arabia still look to Tel Aviv as a partner in NEOM?
It appears that amid ongoing crises in the region, chiefly the Gaza genocide, Riyadh must be careful to avoid being seen as cooperating with the Israelis in covert ways, and full-fledged normalization seems off the table for the foreseeable future.
Nonetheless, after the dust settles in Gaza and the Red Sea security crisis calms down, Saudi Arabia will likely maintain its interest in fostering ties with Israel as part of an “economic normalization” between the two countries. This could be important to Vision 2030’s future, particularly in NEOM.
But Israel’s unprecedented military campaign in Gaza will likely alter West Asia in many ways for decades to come. Even after the current war in Gaza is over, anger toward Israel and the US will continue.
Without a doubt, the Israeli–NEOM connection will be increasingly sensitive and controversial, both in the Kingdom and the wider region – a factor that the leadership in Riyadh cannot dismiss.
By Giorgio Cafiero
Published by The Cradle
Republished by The 21st Century
The views expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of 21cir.com
